Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Arthritis
Arthritis
Inflammation or swelling in the joints is called arthritis. There are more than 100 conditions that cause damage to the joints and other connective tissues. More than one-third of the population in America has arthritis, and this percentage will inevitably rise as the average population age rises. According to the Arthritis Association, Atlanta arthritis is the number 1 cause of disability in most countries. 58.5 million adults in the United States, or almost 1 in 4, have arthritis [1].
Types
Arthritis is divided into more than 100 diverse types. Two of the most common arthritis are osteoarthritis & rheumatoid arthritis. Some types of arthritis are the following.
1. Osteoarthritis
This is one of the common forms of arthritis also called “wear and tear” arthritis, affecting mostly hands, knees, and hips. The connective tissues that connect muscle to bone and keep the joint together are harmed by osteoarthritis, which also affects the bones. The lining of the joint may swell and become inflamed if the cartilage in the joint is significantly damaged. So, bones are at elevated risk of gliding against each other. It results in osteophytes at the end of the bones which are small pieces of bones, which can increase fluid in the joints and the joint capsule may lose its shape due to stretching. Some mutations in the types II, IV, V, and VI collagens can also lead to arthritis [2].
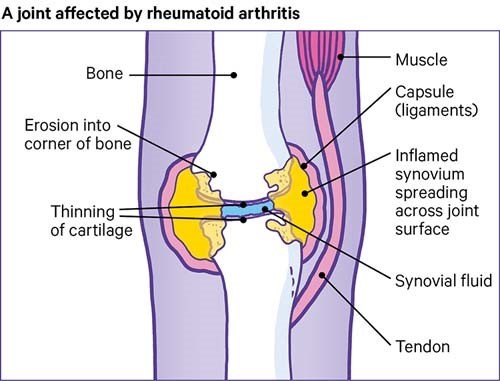
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
It is an auto-immune and inflammatory disorder triggered by our immune system, in which bones and cartilage in joints are destroyed. Age, sex, smoking, obesity, inherited traits, and early childhood birth can increase your risk of getting RA.
A joint affected by RA.
3. Gout
A typical and severe form of inflammatory arthritis is gout in which one joint is affected at a time. One of the main causes of gout is elevated uric acid levels in the blood which causes the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints.
4. Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is characterized by widespread pain across the body, sleep issues, and frequent emotional and mental problems.
5. Childhood Arthritis
Juvenile-idiopathic arthritis is one of the most common types of arthritis affecting children which causes disability by permanently damaging the joints.
6. Thumb Arthritis
Thumb arthritis, also known as the carpometacarpal joint, is a common condition that develops as people age and is caused by the wear and tear of the cartilage at the ends of the bones that make-up the joint at the base of thumb. It causes pain, inflammation, decreased risk of motion and makes simple tasks difficult.
7. Septic Arthritis
Joint inflammation brought on by a bacterial or fungal infection is known as septic arthritis. Hip and knee joints are frequently impacted. It can occur when microbes directly affect joints. Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, or Neisseria gonorrhoeae causes most instances of acute septic arthritis. Chronic septic arthritis is caused by microbe’s candida Albicans and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
8. Psoriatic Arthritis
It is also an autoimmune disorder and sort of spondyloarthritis. Psoriasis skin rash and painful swelling and stiffness in joints are both conditions caused by the immune system. The scalp, buttocks, back, elbows, knees, and other body parts may be impacted by the rash. Severe fatigue is the most common sign of PA.
9. Ankylosing Spondylitis
It is a type of arthritis which mostly affects the spine’s joints, producing discomfort and swelling. In this case, our body can produce more calcium triggered by inflammation, which is used normally to strengthen the bones. The increased calcium in ankylosing spondylitis, cause new bone to form in the spine, which will result in pain and stiffness. This ailment often causes pain in the second half of the night and back swelling that lasts longer than 30 minutes in the morning.
Common symptoms of arthritis
Some common symptoms of arthritis are the following.
- Pain
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Stiffness of joints
- Weakness.
- Fever
- Swelling in the joints
- Redness
- Decreased range of motion
Diagnosis
Arthritis is diagnosed and evaluated by.
- Radiographs
- Laboratory tests
- Inflammatory cases of arthritis are tested for ESR and CRP markers
- Leukocytopenia and thrombocytopenia are common in RA
- Serum analysis can also help for rheumatoid factor, anti-nuclear antibodies, and some peptide antibodies.
- X-rays
- MRI
- Synovial fluid examination [3].
Treatment
Usually, a combination of treatments is used to reduce the pain in the joints. Pharmacological treatments include oral and topical treatment. Topical medications commonly used are capsaicin, topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), topical and duloxetine. Direct injections of corticosteroids into the joint are possible. Topical NSAIDs, capsaicin, and other ointments are typically used as first-line treatments; oral NSAIDs should only be used if these treatments are ineffective or if the condition is more systemic. Early use of biologics, glucocorticoids, and disease-modifying anti-rheumatic medications (DMARDs) is more successful than treatment with these drugs. Anti-inflammatory drug use can offer significant relief and should ideally be started within 24 hrs of an acute gouty flare. Oral corticosteroids, NSAIDs like indomethacin or high-dose naproxen, or colchicine are some of them. For a patient with a particular involvement, intra-articular corticosteroid injections may be helpful; however, if the patient is unable to take drugs orally, intramuscular, or intravenous corticosteroids may be administered. Patients with recurring flares, chronic renal disease, nephrolithiasis, or tophi are advised to take uric acid-lowering medications instead of treating acute flares because they are more likely to cause these conditions [4].
Risk Factors and Ways to Reduce Arthritis
Risk factors which you can control to minimize the risk of arthritis are overweight and obesity, infection, joint injuries, occupation, and smoking.
- Reduce weight and maintain a normal BMI
- Routine check-ups can reduce the risk of getting arthritis from bacteria and viruses such as salmonella, shigella, chlamydia, gonorrhea and hepatitis C which can affect joints.
- Quit smoking
- Participating in joint-friendly physical activity can reduce pain
- Do regular exercise. It is recommended that adults should exercise 150 minutes of moderate exercise a week
- Must understand self-management
The risk of getting arthritis cannot be controlled in the case of genetics, gender, and ageing. Most types of arthritis affect mostly women, worsened by ageing and specific genotype can make this case even worse.
Hyperbaric Oxygen as Effective Medicine for Arthritis
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) uses pure oxygen at elevated pressure (often 2-3 atmospheres), increasing the amount of oxygen in the blood and tissues (Hyperoxia). A therapeutic method called hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) relies on exposure to pure oxygen (O2) concentrations in elevated atmospheric pressure. This pressure could be greater than or equivalent to 1.4 atmospheres (atm), as per the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS). All currently UHMS-approved indications, however, need for patients to breathe entirely with oxygen while confined in a space with a least 2 ATA of pressure [5]. A pressure environment larger than the air pressure at sea level must be present for hyperbaric medicine to be effective. To lessen the harmful effects of systemic gas bubbles, the treatment includes therapeutic recompression for decompression illness and hyperbaric oxygen therapy or HBOT is a process in medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure basically higher than atmospheric pressure. By physically reducing the size of the bubbles and improving the conditions for bubble and excess dissolved gas elimination, these procedures aim to treat decompression illness. The necessary tools for hyperbaric oxygen therapy are a pressure chamber, which may be flexible or rigid in design, and a way to administer 100% oxygen. Trained professionals watch the patient and carry out the operation according to a predefined plan, making necessary schedule adjustments.
People with arthritis have been reported to benefit from hyperbaric oxygen therapy. It can lessen the discomfort and irritation that individuals with osteoarthritis experience. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy helps prevent the immune system’s self-destruction caused by rheumatoid arthritis. Many studies on animal models such as rats and mice were reported with the context of improvement of arthritis when treated with hyperbaric oxygen. One such study reported that in a rat model of arthritis, hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces pain and inflammation. The amplitude of the effects of acetylsalicylic acid treatment and hyperbaric oxygen therapy are extremely similar [6].
Patients with arthritis and osteoarthritis benefit from hyperbaric oxygen therapy because it has a variety of physiological effects on the body. Because it is an essential molecule for the formation and maturation of the collagen fiber, producing a more stable fibrillar structure, hyperbaric oxygen reduces the degree of cartilage damage. Additionally, studies have demonstrated that hyperbaric oxygenation reduces cell death, which causes articular cartilage to deteriorate. Contrarily, hyperbaric oxygen therapy has an immunomodulatory impact that reduces the body’s own immune cells’ ability to attack its tissue. According to many studies, hyperbaric oxygen therapy enhances stem cell release and stimulates their differentiation into various tissues, which may aid in the healing of the injured joint. In a pilot study on 3 individuals, recovery from arthritis and pain was seen with hyperbaric medicine (2 ATA) [7]. In another study on humans, for 6 to 10 weeks, ten RA patients had 30 HBO2 sessions. Based on data from several, established clinical assessments, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (1.8 ATA) was seen as beneficial for treating joint discomfort in RA patients [8].
Some benefits of hyperbaric oxygen reported in the literature are reduction in inflammation, pain relief, immunomodulatory effect, tissue regeneration and promote recovery and mobility of joints. The capacity of hyperbaric oxygen therapy to lessen oxidative stress in a local hypoxic condition is a promising mechanism. In addition to increasing the expression of the apoptosis-regulating gene Bcl-2, this treatment inactivates caspase 3 and caspase 9. Accordingly, hyperbaric oxygen therapy may improve cellular oxygen availability, lessen the apoptosis caused by mitochondria, and maintain mitochondrial activity. Consequently, the decreased levels of inflammatory cytokines appear to result in an overall improvement in functioning and a decrease in discomfort in patients [9].

References
1. Ma L, Cranney A, Holroyd-Leduc JM. Acute monoarthritis: what is the cause of my patient’s painful swollen joint? CMAJ. 2009 Jan 06;180(1):59-65.
Doi: 10.1503/cmaj.080183
Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2612045/
2. Reginato AM, Olsen BR. The role of structural genes in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritic disorders. Arthritis Res. 2002;4(6):337-45.
Doi: 10.1186/ar595
Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC153840/
[3]. Bas S, Genevay S, Meyer O, Gabay C. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, IgM and IgA rheumatoid factors in the diagnosis and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003 May;42(5):677-80.
DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg184
Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518992/
[4]. Neogi T. Clinical practice. Gout. N Engl J Med. 2011 Feb 03;364(5):443-52.
[5]. UHMS Position Statement: Low-Pressure Fabric Hyperbaric Chambers Title: Low-Pressure Fabric Hyperbaric Chambers. 2017. [(accessed on 23 May 2021)]. Available online: https://www.uhms.org/images/Position-Statements/UHMS_Position_Statement_LP_chambers_revised.pdf
[6]. Wilson HD, Toepfer VE, Senapati AK, Wilson JR, Fuchs PN. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment is comparable to acetylsalicylic acid treatment in an animal model of arthritis. The Journal of Pain. 2007 Dec 1;8(12):924-30.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2007.06.005
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1526590007007353
[7]. Slade JB, Potts MV, Flower AM, Sit MT, Schmidt TW. Pain improvement in rheumatoid arthritis with hyperbaric oxygen: report of three cases. Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine: Journal of the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society, Inc. 2016 Jul 1;43(4):467-72.
Link: https://europepmc.org/article/med/28763177
[8]. Sit, Michelle T. MD∗; Schmidt, Thomas W. MD†; Edmonds, Lance D. MD∗; Kelly, Jason A. MD‡; Sky, Karen M. MD§; Thornton, Jennifer A. PhD‡; McNeary-Garvin, Antoinette M. MSN‡; Thom, Stephen R. MD, PhD∥; Slade, John B. MD‡. The Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen on Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Study. JCR: Journal of Clinical Rheumatology: December 2021 – Volume 27 – Issue 8 – p e462-e468
doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000001540
DOI: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000001540
[9]. E. Palzur, M. Zaaroor, E. Vlodavsky, F. Milman, and J. F. Soustiel, “Neuroprotective effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in brain injury is mediated by preservation of mitochondrial membrane properties,” Brain Research, vol. 1221, pp. 126– 133, 2008.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1582432
Link: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2022/1582432/